Financial literacy worldwide has gained increasing importance over the past decade, particularly following the global financial crisis of 2008, which highlighted the critical role financial education plays in maintaining economic and financial stability. In Lebanon, financial literacy among citizens remains relatively low, with significant gaps in understanding basic financial concepts such as inflation, interest rates, and financial planning.
Since 2013, efforts to enhance financial literacy and education among the population in Lebanon have been spearheaded by key national institutions, including the Institut des Finances Basil Fuleihan (IoF), the Ministry of Education and Higher Education (MoEHE), the Ministry of Economy and Trade, the Ministry of Social Affairs, the Association of Banks in Lebanon (ABL), as well as various NGOs and training institutions.
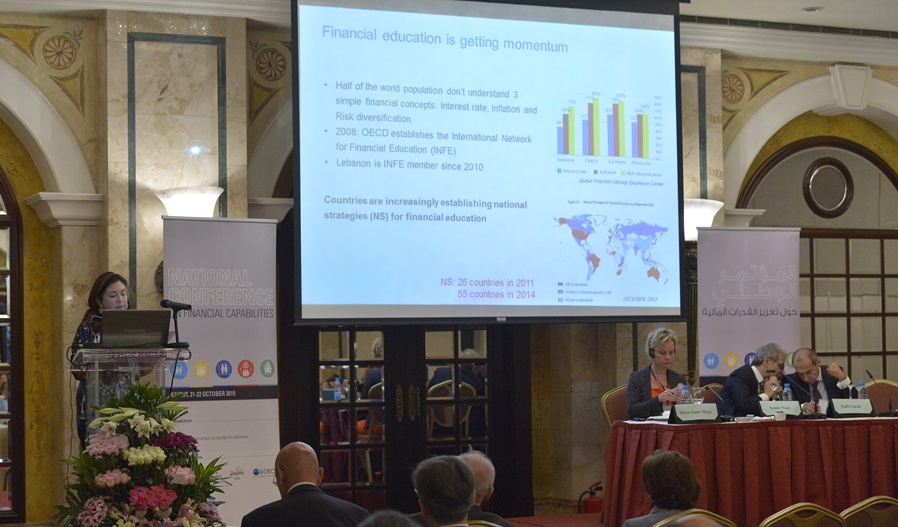
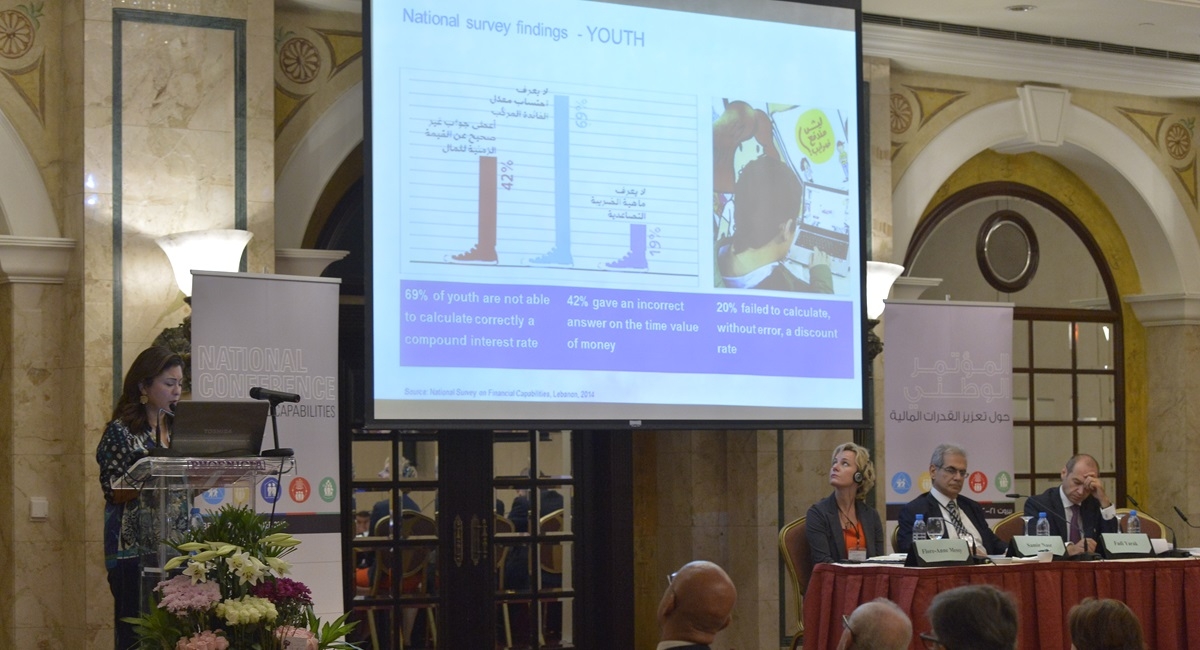
The first step involved the compilation of national data on financial literacy and inclusion, using the findings of the national survey measuring financial literacy in Lebanon conducted by the Institute between 2011 and 2012, among other local and international sources.
Between 2013 and 2015, a series of consultation meetings bringing together stakeholders from diverse sectors, including the public sector, financial institutions, academia, NGOs, and international organizations were held aiming to gather qualitative feedback on the financial education needs of various population segments, and to develop recommendations for improving financial literacy in Lebanon. A key focus of these discussions was the importance of forging partnerships between the public and private sectors to ensure a holistic approach to financial literacy.
These efforts culminated in the National Conference on Financial Capabilities, held in October 2015, which was jointly organized by the IoF, ABL, the Ministry of Finance, MEHE, and the OECD’s International Network on Financial Education (INFE). The conference resulted in concrete recommendations that laid the groundwork for the "National Strategy for Financial Education", which was formalized for the period 2016-2019. The strategy was structured around five main pillars, each targeting a different aspect of financial literacy and economic inclusion:
1. Promoting Financial Literacy: this pillar focused on integrating financial education into school curricula to equip future generations with essential financial knowledge.
2. Improving Consumer Protection: this pillar aimed to ensure that citizens understood their rights and responsibilities when dealing with financial products and services.
3. Encouraging Long-term Savings and Enhancing Pension Schemes: this pillar aimed to raise awareness about the importance of long-term savings and strengthen the social protection system, particularly for workers in the private sector who lack access to formal pension plans.
4. Improving Governance and Citizenship: this pillar aimed to enhance citizens' understanding of fiscal policies and public finance, promoting greater transparency and accountability in government.
5. Increasing Financial Inclusion for Underprivileged Groups: this pillar sought to improve access to formal financial services for marginalized populations including low-income families, rural residents and people with special needs.
The National Strategy for Financial Education represents a collaborative effort among Lebanon’s major stakeholders, including government bodies, the banking sector, and civil society, to address the country’s financial literacy challenges